The research group led by Karl Kuchler at the Max Perutz Labs, a joint venture of the Medical University of Vienna and the University of Vienna, has discovered for the first time, how the fungus Candida glabrata can tap the host iron pools and use this essential metal ion scavenged from immune cells to escape immune defenses. These results have been published in the journal "Cell Host & Microbe" and also point to potential new ways of combating the pathogenic fungus in the human host by blocking iron accumulation in the pathogen.
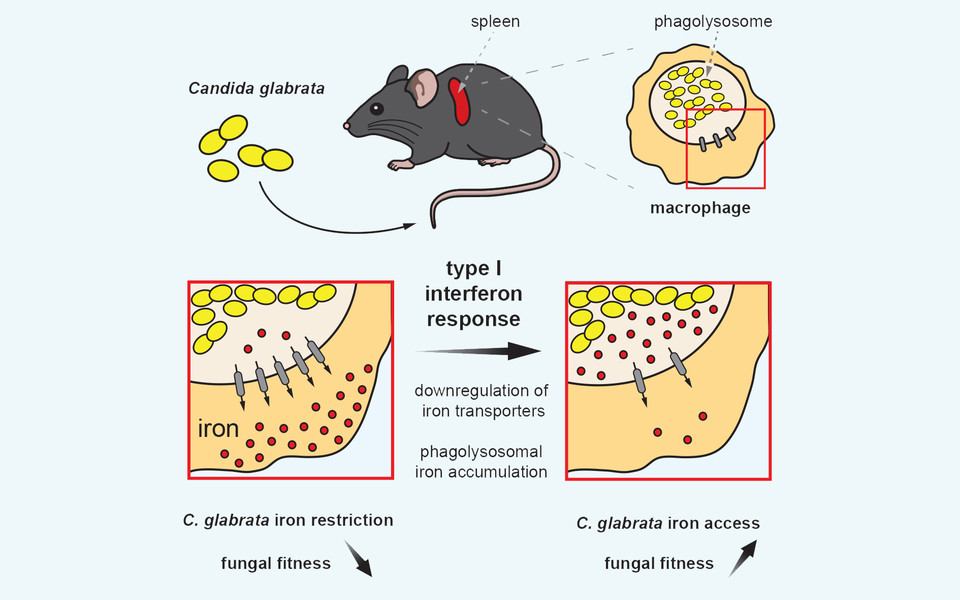
Trace elements such as iron are essential for all higher cells including humans, but are extremely toxic at high concentrations. For example, iron is a central component of haemoglobin, the essential molecule for oxygen transport within the body. However, microbial pathogens also require trace elements to sustain their own growth and survival once a host is infected. Thus, both host and the pathogen are competing for iron sources. Owing to its potential toxicity, the host immune response restrains iron pools by sequestering iron in dedicated storage organelles such as so-called phagolysosomes, which is also the organelle where engulfed pathogens are cleared. Eating machines of the immune defense, so called macrophages, play a central role in iron metabolism. Further, macrophages use specialised mechanisms for microbial clearance within defined organelles (phagolysosomes) as for instance through oxidative stress. Additionally, when macrophages have taken up intracellular fungal pathogens into phagolysosomes for fungal killing, surplus iron is also shuttled out of these organelles by iron transport proteins, in order to impede the growth of the fungus.
The group led by Karl Kuchler and lead author Michael Riedelberger now show that the host immune response by the so-called type I interferons dysregulate the host iron metabolism upon infections by Candida glabrata. Interferons are immune signaling molecules which control microbial and fungal infections. However, infections by Candida glabrata set-off interferons that disrupt normal expression of iron transport proteins in macrophages. Therefore, iron inadvertently accumulates within phagolysosomes of macrophages, thereby facilitating iron scavenging by the pathogen. Consequently, Candida glabrata can exploit phagolysosomal iron pools, thus promoting fungal replication and survival from immune defenses. A single macrophage can engulf up to 50 fungal cells, which can survive within this immune cell for months. Of note, physical damage of infected macrophages can further promote the dissemination of Candida glabrata within the host and therefore enhances the fungal dissemination.
The scientists identified two fungal transporters that are central for fungal iron acquisition by the pathogen. “Blocking the ability of Candida glabrata to scavenge iron from the host by genetically removing these iron uptake transporters abrogates the ability of Candida glabrata to survive in the host" explains Karl Kuchler. The researchers conclude that it might be possible to identify therapeutic compounds to inhibit these fungal iron transporters, thus promising new therapeutic options for multidrug-resistant fungal pathogens such as Candida glabrata.
Publication:
Michael Riedelberger, Philipp Penninger, Michael Tscherner, Markus Seifert, Sabrina Jenull, Carina Brunnhofer, Bernhard Scheidl, Irina Tsymala, Christelle Bourgéois, Andriy Petryshyn, Walter Glaser, Andreas Limbeck, Birgit Strobl, Guenter Weiss, and Karl Kuchler: Type I interferon response dysregulates host iron homeostasis and enhances Candida glabrata infection. Cell Host & Microbe (2020)