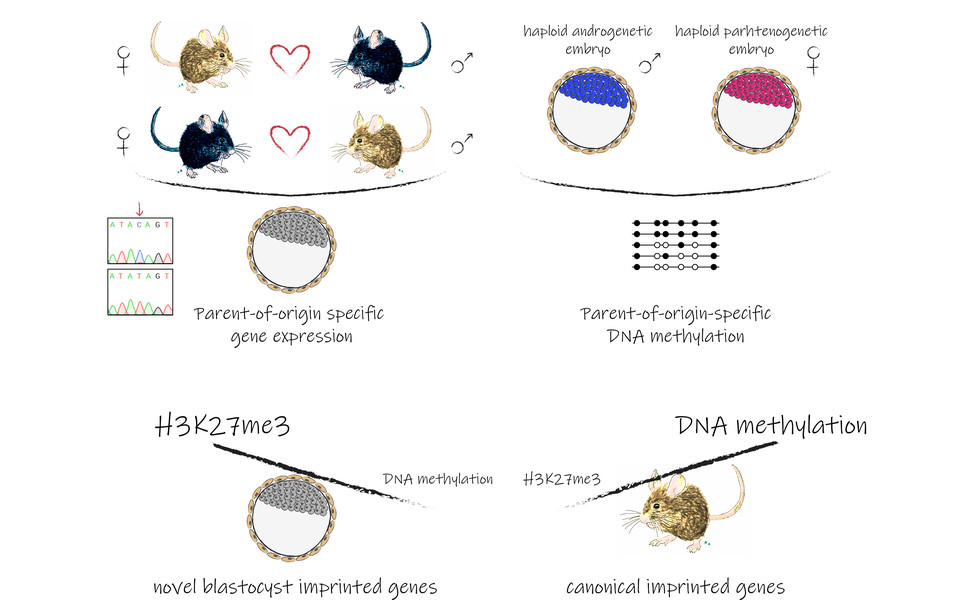
We all inherit traits from our parents, but not only as one set of genes from our father and one from our mother. Epigenetic marks change the way our genes work – without altering the DNA sequence. For most genes, both copies of the gene are active, but a minority of genes is exclusively expressed from either the maternal or paternal allele. The epigenetic mechanism first attributed to this phenomenon, termed genomic imprinting, was DNA methylation. Methylation occurs primarily on cytosine, one of the four bases that together make up our genetic code, and typically leads to the repression of transcription. However, a second mechanism implicated in imprinting relies on histone modifications. Here, it is the methylation of histone proteins that changes the transcriptional activity of genes. “Historically, DNA methylation has been the subject of most imprinting studies, but in recent years it has been reported that trimethylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 is an important imprinting mark”, explains co-first author Laura Santini. Hundreds of imprinted genes have been identified and defects in imprinting are implicated in several developmental disorders.
In cooperation with Florian Halbritter from the St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute and Tony Perry from the University of Bath, the scientists have now identified 71 novel imprinted genes and profiled their methylation status. “We realized that the majority of the novel genes with uniparental expression in preimplantation blastocyst were not residing in close proximity to methylation marks, implying that DNA methylation was not the major driver of imprinting at this developmental stage”, says Laura Santini. The team found out that also some of the genes historically associated with DNA methylation are actually regulated by H3K27 trimethylation specifically in blastocysts. This suggests that histone modifications play a more significant role in early development than previously thought.
The fundamental reasons for imprinting mechanisms are still, largely, a mystery, and the precise mechanisms involved in the regulation of imprinted genes are not fully understood. H3K27 trimethylation is a reversible modification, and many of the imprinted genes lose their H3K27 marks during development. DNA methylation on the other hand is a more stable mark, but the levels in pre-implantation blastocysts are low. “It seems that histone modification may serve as a backup system to ensure that imprinting is maintained during early development before DNA methylation takes over as the primary imprinting mechanism”, concludes group leader Martin Leeb.
Publication:
Laura Santini, Florian Halbritter, Fabian Titz-Teixeira, Toru Suzuki, Maki Asami, Xiaoyan Ma, Julia Ramesmayer, Andreas Lackner, Nick Warr, Florian Pauler, Simon Hippenmeyer, Ernest Laue, Matthias Farlik, Christoph Bock, Andreas Beyer, Anthony C. F. Perry and Martin Leeb: Novel imprinted genes exemplify predominantly H3K27me3- dependent imprinting in mouse blastocysts. Nature Communications 2021