Selected Publications
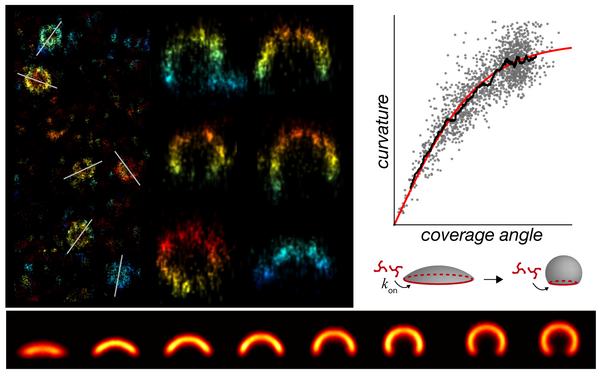
Continuum architecture dynamics of vesicle tethering in exocytosis
Puig-Tintó, M., S. Ortiz, S. Meek, R. Coray, L.I. Betancur, A.C. Hernández, A. Castellet, E. Kramer, P. Hoess, M. Mund, A. Molina-Ribagorda, M. Izquierdo-Serra, B. Oliva, A. De Marco, J. Ries*, D. Castaño-Díez,* C. Manzo*, and O. Gallego*.
Evaluating MINFLUX experimental performance in silico
2025, Nature Communications 17 (December 2025): 246
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-66952-w
Zach Marin, and Jonas Ries.
MINFLUX Achieves Molecular Resolution with Minimal Photons.
2025, Nature Photonics 19, no. 3 (March 2025): 238–47.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01625-0
Scheiderer, Lukas, Zach Marin, and Jonas Ries.
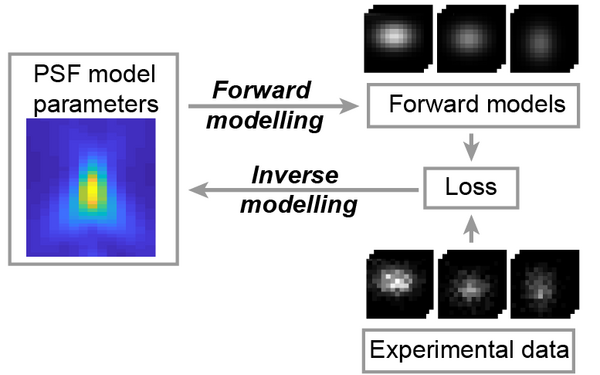
Universal inverse modeling of point spread functions for SMLM localization and microscope characterization.
2024 Nature methods;21(6):1082, 1093, 1082-1093.
PMID: 38831208
Liu Sheng, Chen Jianwei, Hellgoth Jonas, Müller Lucas-Raphael, Ferdman Boris, Karras Christian, Xiao Dafei, Lidke Keith A, Heintzmann Rainer, Shechtman Yoav, Li Yiming, Ries Jonas
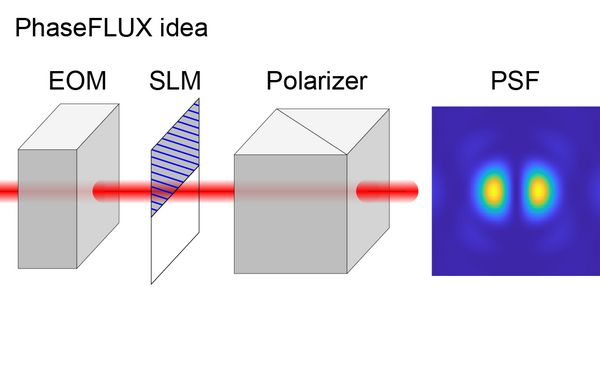
Simple and robust 3D MINFLUX excitation with a variable phase plate.
2024 Light, science & applications;13(1):134.
PMID: 38849346
Deguchi Takahiro, Ries Jonas
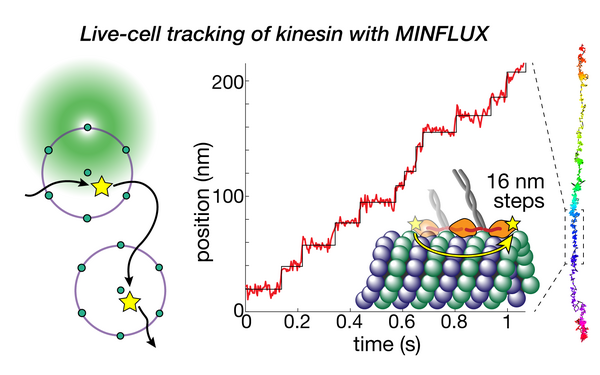
Direct observation of motor protein stepping in living cells using MINFLUX.
2023 Science (New York, N.Y.)(6636)
PMID: 36893247
Deguchi Takahiro, Iwanski Malina K, Schentarra Eva-Maria, Heidebrecht Christopher, Schmidt Lisa, Heck Jennifer, Weihs Tobias, Schnorrenberg Sebastian, Hoess Philipp, Liu Sheng, Chevyreva Veronika, Noh Kyung-Min, Kapitein Lukas C, Ries Jonas
Maximum-likelihood model fitting for quantitative analysis of SMLM data.
2023 Nature methods(1)
PMID: 36522500
Wu Yu-Le, Hoess Philipp, Tschanz Aline, Matti Ulf, Mund Markus, Ries Jonas
Nanoscale structural organization and stoichiometry of the budding yeast kinetochore.
2023 The Journal of cell biology(4)
PMID: 36705601
Cieslinski Konstanty, Wu Yu-Le, Nechyporenko Lisa, Hörner Sarah Janice, Conti Duccio, Skruzny Michal, Ries Jonas
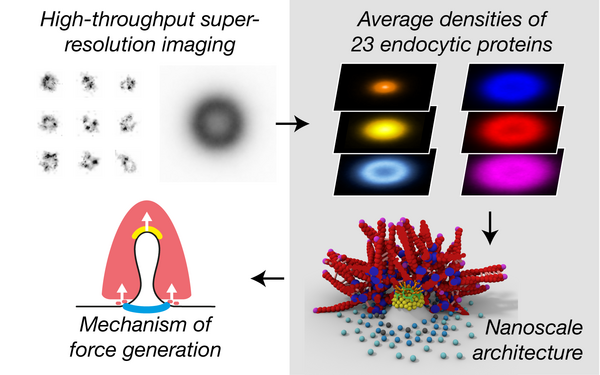
Clathrin coats partially preassemble and subsequently bend during endocytosis.
2023 The Journal of cell biology(3)
PMID: 36734980
Mund Markus, Tschanz Aline, Wu Yu-Le, Frey Felix, Mehl Johanna L, Kaksonen Marko, Avinoam Ori, Schwarz Ulrich S, Ries Jonas
Global fitting for high-accuracy multi-channel single-molecule localization.
2022 Nature communications(1)
PMID: 35668089
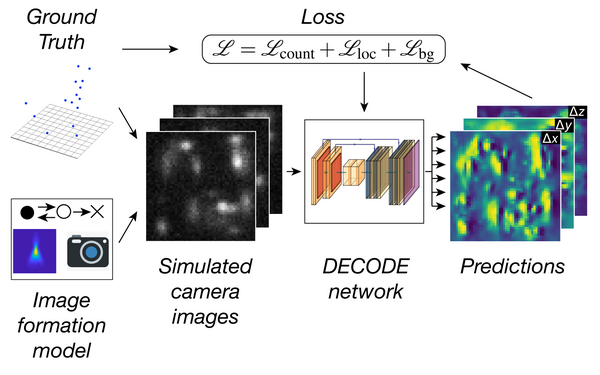
Li Yiming, Shi Wei, Liu Sheng, Cavka Ivana, Wu Yu-Le, Matti Ulf, Wu Decheng, Koehler Simone, Ries Jonas
Deep learning enables fast and dense single-molecule localization with high accuracy.
2021 Nature methods(9)
PMID: 34480155
Speiser Artur, Müller Lucas-Raphael, Hoess Philipp, Matti Ulf, Obara Christopher J, Legant Wesley R, Kreshuk Anna, Macke Jakob H, Ries Jonas, Turaga Srinivas C
MINFLUX nanoscopy delivers 3D multicolor nanometer resolution in cells.
2020 Nature methods(2)
PMID: 31932776
Gwosch Klaus C, Pape Jasmin K, Balzarotti Francisco, Hoess Philipp, Ellenberg Jan, Ries Jonas, Hell Stefan W
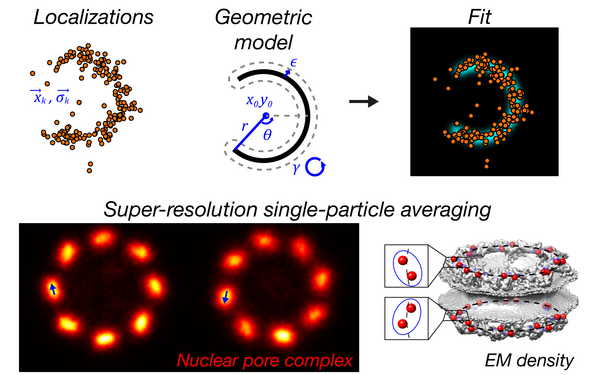
Nuclear pores as versatile reference standards for quantitative superresolution microscopy.
2019 Nature methods(10)
PMID: 31562488
Thevathasan Jervis Vermal, Kahnwald Maurice, Cieśliński Konstanty, Hoess Philipp, Peneti Sudheer Kumar, Reitberger Manuel, Heid Daniel, Kasuba Krishna Chaitanya, Hoerner Sarah Janice, Li Yiming, Wu Yu-Le, Mund Markus, Matti Ulf, Pereira Pedro Matos, Henriques Ricardo, Nijmeijer Bianca, Kueblbeck Moritz, Sabinina Vilma Jimenez, Ellenberg Jan, Ries Jonas
View all Publications of Group Ries